Import
|
By Country
|
The term import is derived from the conceptual meaning as to bring in the goods and services into the port of a country. The buyer of such goods and services is referred to an "importer" who is based in the country of import whereas the overseas based seller is referred to as an "exporter". [1] Thus an import is any good (e.g. a commodity) or service brought in from one country to another country in a legitimate fashion, typically for use in trade. It is a good that is brought in from another country for sale.[2] Import goods or services are provided to domestic consumers by foreign producers. An import in the receiving country is an export to the sending country.
Imports, along with exports, form the basis of international trade. Import of goods normally requires involvement of the customs authorities in both the country of import and the country of export and are often subject to import quotas, tariffs and trade agreements. When the "imports" are the set of goods and services imported, "Imports" also means the economic value of all goods and services that are imported. The macroeconomic variable I usually stands for the value of these imports over a given period of time, usually one year.
Contents |
Definition
"Imports" consist of transactions in goods and services (sales, barter, gifts or grants) from non-residents residents to residents.[3] The exact definition of imports in national accounts includes and excludes specific "borderline" cases. [4] A general delimitation of imports in national accounts is given below:
- An import of a good occurs when there is a change of ownership from a non-resident to a resident; this does not necessarily imply that the good in question physically crosses the frontier. However, in specific cases national accounts impute changes of ownership even though in legal terms no change of ownership takes place (e.g. cross border financial leasing, cross border deliveries between affiliates of the same enterprise, goods crossing the border for significant processing to order or repair). Also smuggled goods must be included in the import measurement.
- Imports of services consist of all services rendered by non-residents to residents. In national accounts any direct purchases by residents outside the economic territory of a country are recorded as imports of services; therefore all expenditure by tourists in the economic territory of another country are considered as part of the imports of services. Also international flows of illegal services must be included.
Basic trade statistics often differ in terms of definition and coverage from the requirements in the national accounts:
- Data on international trade in goods are mostly obtained through declarations to custom services. If a country applies the general trade system, all goods entering the country are recorded as imports. If the special trade system (e.g. extra-EU trade statistics) is applied goods which are received into customs warehouses are not recorded in external trade statistics unless they subsequently go into free circulation of the importing country.
- A special case is the intra-EU trade statistics. Since goods move freely between the member states of the EU without customs controls, statistics on trade in goods between the member states must be obtained through surveys. To reduce the statistical burden on the respondents small scale traders are excluded from the reporting obligation.
- Statistical recording of trade in services is based on declarations by banks to their central banks or by surveys of the main operators. In a globalized economy where services can be rendered via electronic means (e.g. internet) the related international flows of services are difficult to identify.
- Basic statistics on international trade normally do not record smuggled goods or international flows of illegal services. A small fraction of the smuggled goods and illegal services may nevertheless be included in official trade statistics through dummy shipments or dummy declarations that serve to conceal the illegal nature of the activities.
Balance of trade
Balance of trade represents a difference in value for import and export for a country. A country has demand for an import when domestic quantity demanded exceeds domestic quantity supplied, or when the price of the good (or service) on the world market is less than the price on the domestic market.
The balance of trade, usually denoted 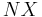 , is the difference between the value of the goods (and services) a country exports and the value of the goods the country imports:
, is the difference between the value of the goods (and services) a country exports and the value of the goods the country imports:
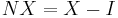 , or equivalently
, or equivalently 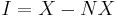
A trade deficit occurs when imports are large relative to exports. Imports are impacted principally by a country's income and its productive resources. For example, the US imports oil from Canada even though the US has oil and Canada uses oil. However, consumers in the US are willing to pay more for the marginal barrel of oil than Canadian consumers are, because there is more oil demanded in the US than there is oil produced.
In macroeconomic theory, the value of imports 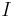 can be modeled as a function of the domestic absorption
can be modeled as a function of the domestic absorption  and the real exchange rate
and the real exchange rate 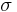 . These are the two largest factors of imports and they both affect imports positively:
. These are the two largest factors of imports and they both affect imports positively:
Types of import
There are two basic types of import:
- Industrial and consumer goods
- Intermediate goods and services
Companies import goods and services to supply to the domestic market at a cheaper price and better quality than competing goods manufactured in the domestic market. Companies import products that are not available in the local market.
There are three broad types of importers:
- Looking for any product around the world to import and sell.
- Looking for foreign sourcing to get their products at the cheapest price.
- Using foreign sourcing as part of their global supply chain.
Direct-import refers to a type of business importation involving a major retailer (e.g. Wal-Mart) and an overseas manufacturer. A retailer typically purchases products designed by local companies that can be manufactured overseas. In a direct-import program, the retailer bypasses the local supplier (colloquial middle-man) and buys the final product directly from the manufacturer, possibly saving in added costs. This type of business is fairly recent and follows the trends of the global economy.
Statistical data
Data on the value of imports and their quantities often broken down by detailed lists of products are available in statistical collections on international trade published by the statistical services of intergovernmental organisations (e.g. UNSTAT, FAOSTAT, OECD), supranational statistical institutes (e.g. Eurostat) and national statistical institutes.
See also
References
- ^ Joshi, Rakesh Mohan, (2009) International Business, Oxford University Press, New Delhi and New York ISBN 0195689097
- ^ Sullivan, Arthur; Steven M. Sheffrin (2003). Economics: Principles in action. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458: Pearson Prentice Hall. pp. 552. ISBN 0-13-063085-3. http://www.pearsonschool.com/index.cfm?locator=PSZ3R9&PMDbSiteId=2781&PMDbSolutionId=6724&PMDbCategoryId=&PMDbProgramId=12881&level=4.
- ^ Lequiller, F; Blades, D.: Understanding National Accounts, Paris: OECD 2006, pp. 139-143
- ^ for example, see Eurostat: European System of Accounts - ESA 1995, §§ 3.128-3.146, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg, 1996
- ^ Burda, Wyplosz (2005): Macroeconomics: A European Text, Fourth Edition, Oxford University Press